Communication-Avoiding Machine Learning
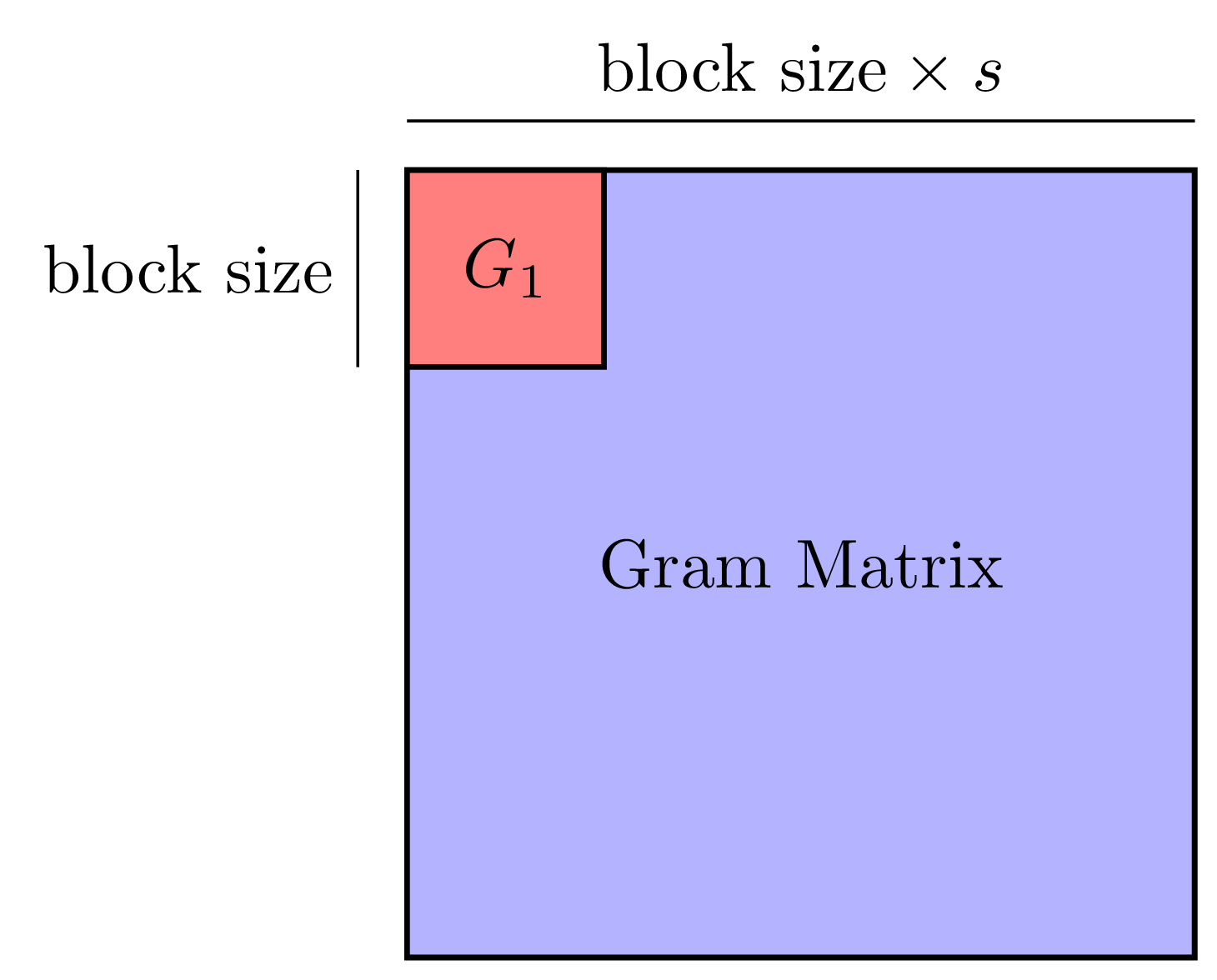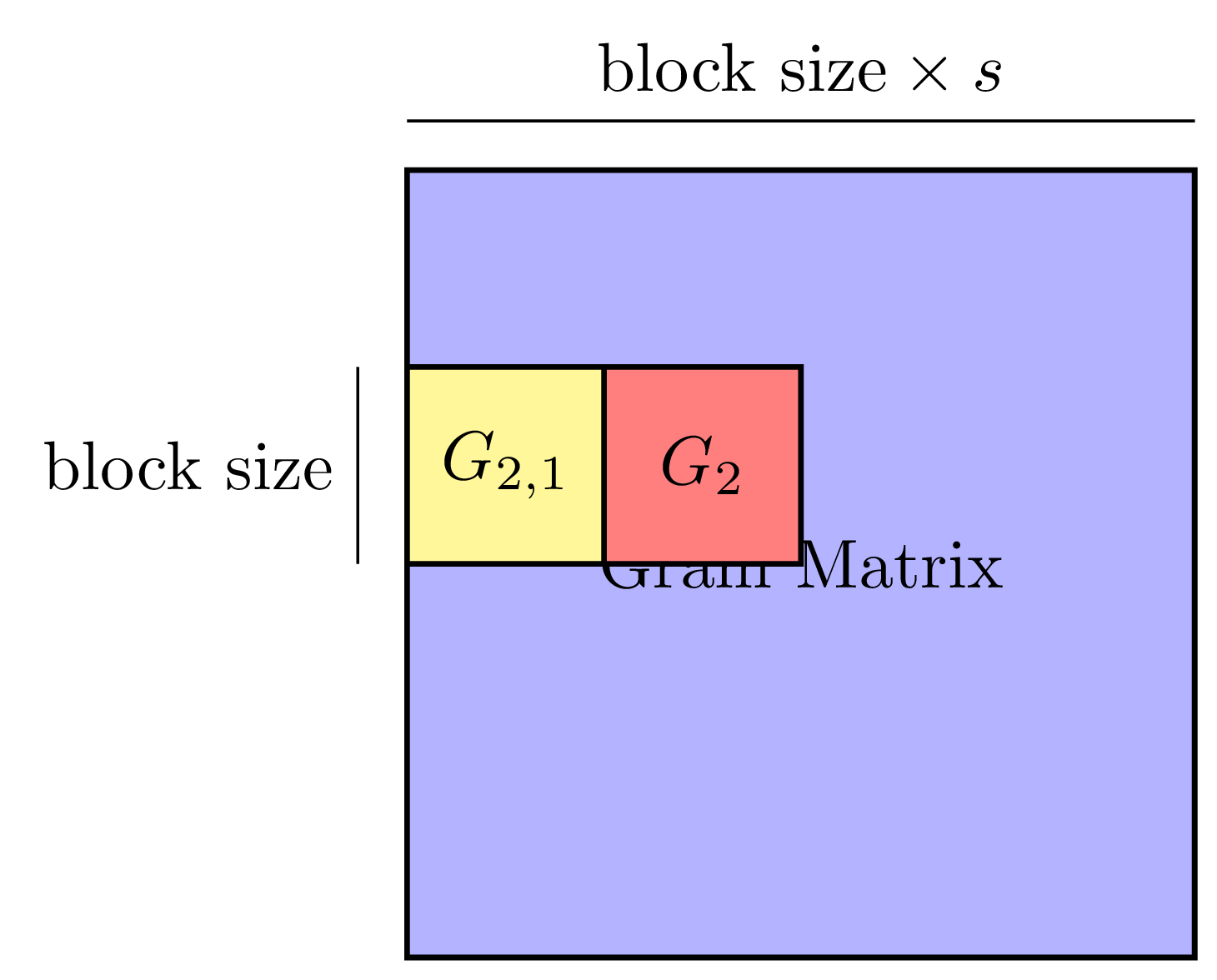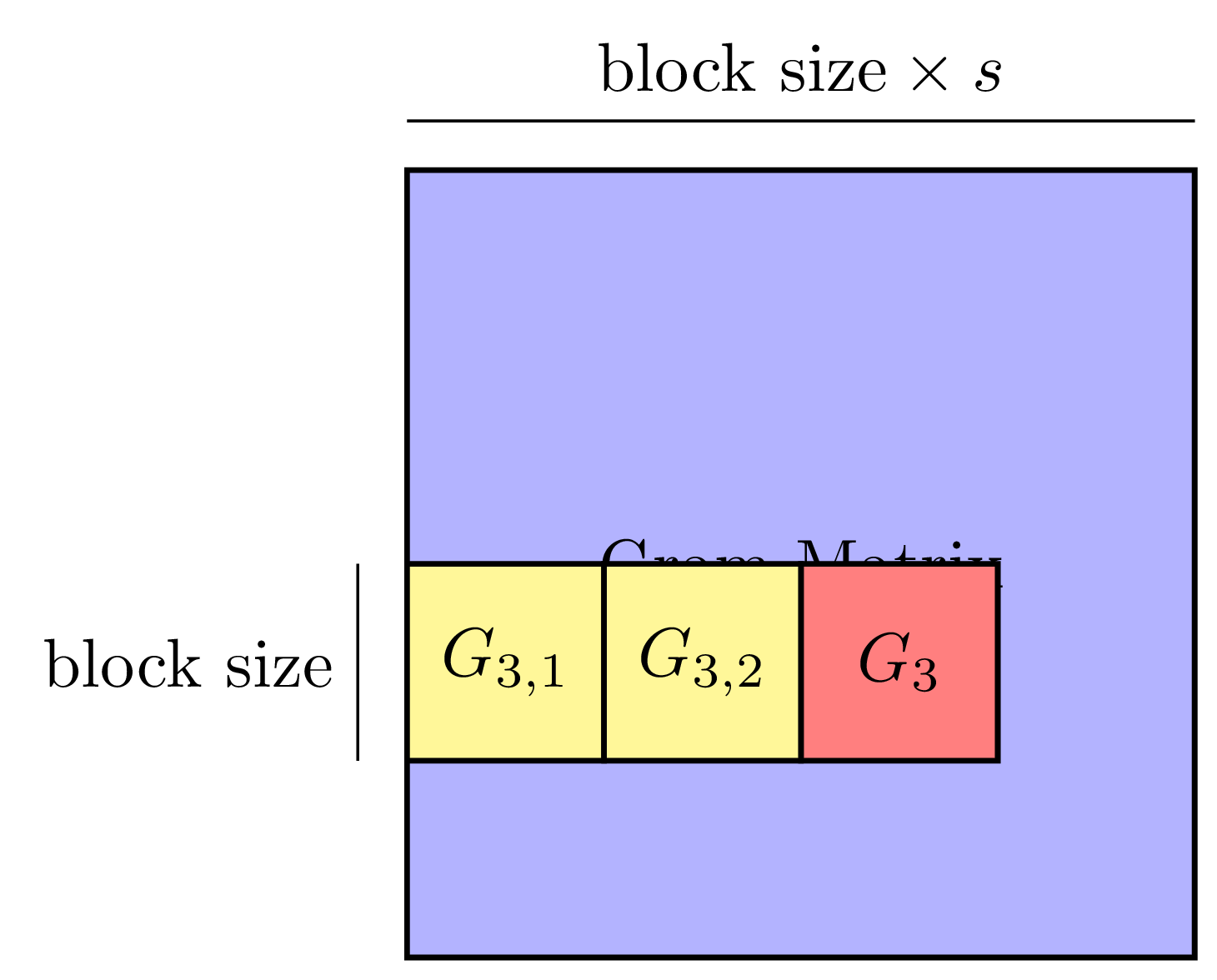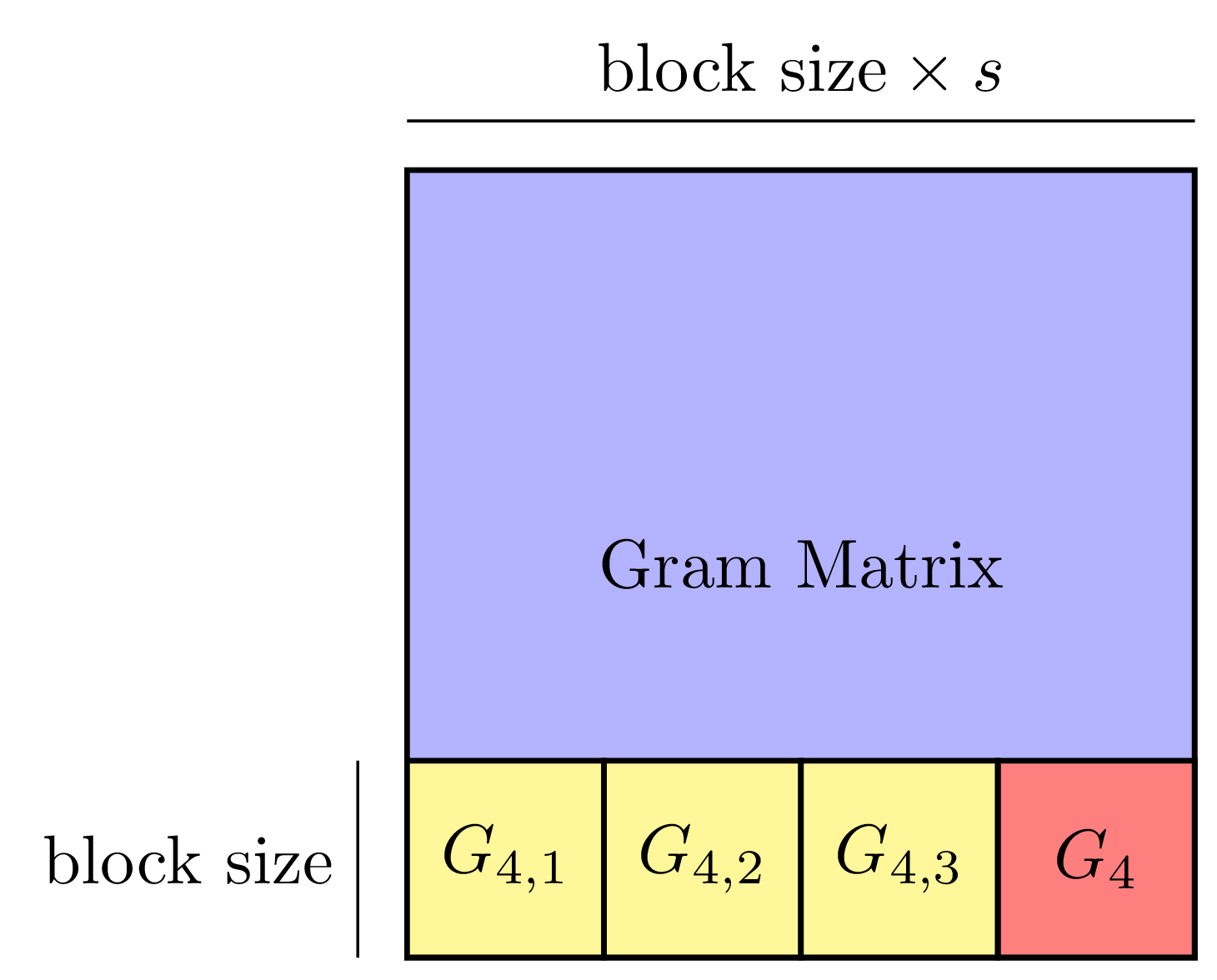
Machine learning has gained renewed interest in recent years due to advances in computer hardware (processing power and high-bandwidth storage) and the availability of large amounts of data which can be used to develop accurate, robust models. While hardware improvements have facilitated the development of machine learning models on a single machine, the analysis of large amounts of data still requires parallel computers to obtain shorter running times.
This project focuses on developing novel techniques and algorithms to reduce the communication bottleneck when performing machine learning tasks at scale on parallel machines. Topics in this area include: i) redesigning existing machine learning algorithms to reduce communication, ii) studying the asymptotic and numerical behavior of these algorithms, and iii) implementing these algorithms as part of a high performance software library.
Scalable Deep Learning
Deep learning is the enabling technology behind many applications that we use daily, from FaceID (Image Recognition) and Alexa (Voice Recognition) to Autopilot (Self-Driving Cars). All of these technologies (and many more) utilize deep learning models under the hood to solve complex optimization problems with high accuracy, in some cases, superhuman accuracy.
Large deep learning models are trained on multi-node, multi-GPU machines and require several days of training. This project focuses on developing new training techniques, optimization problems, and computational kernels to improve performance. Topics in this area include: i) implementing new (quasi) second-order optimization methods, ii) redesigning optimization methods to reduce communication, and iii) implementing new matrix and tensor factorizations to compress and speedup training.
